An introduction to biosimilar medicines
Understand the similarities between biologic medicines and biosimilars in terms of structure, mode of action, efficacy and safety.
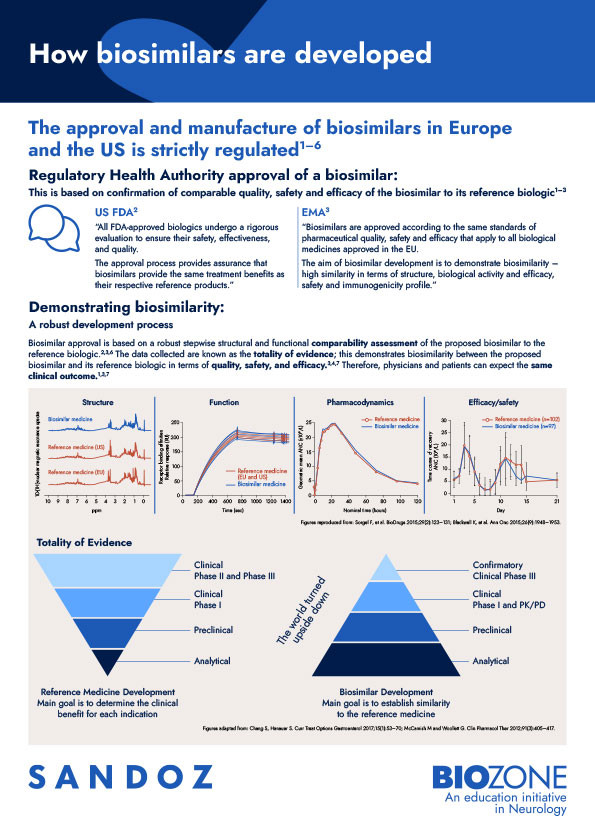
This infographic highlights the strictly regulated biosimilar approval process, which assesses biosimilarity on the basis of the totality of evidence.
To maintain consistent product quality and activity, a biosimilar medicine must be made in accordance with good manufacturing practice for producing, processing, packaging, or storage of a drug product.1
The US FDA and EMA evaluate biosimilarity based on the totality of evidence versus the original-brand biologic. The totality of evidence includes assessment of all of a biosimilar’s chemical and clinical aspects compared with the reference biologic medicine.2,3
References:
1. FDA. CGMP regulations. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/pharmaceutical-quality-resources/current-good-manufacturing-practice-cgmp-regulations. [Last accessed April 2022].
2. FDA. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/FDA%E2%80%99s-Overview-of-the-Regulatory-Guidance-for-the-Development-and-Approval-of-Biosimilar-Products-in-the-US.pdf. [Last accessed April 2022].
3. EMA. Biosimilars in the EU. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/leaflet/biosimilars-eu-information-guide-healthcare-professionals_en.pdf. [Last accessed February 8 2022]
These materials are intended for healthcare professionals only. This page is sponsored by Sandoz.
MLR: 215945
Understand the similarities between biologic medicines and biosimilars in terms of structure, mode of action, efficacy and safety.
Test your knowledge on the development processes of biosimilar medicines in this interactive quiz.