The clinical development process of biosimilar medicines
This infographic highlights the strictly regulated biosimilar approval process, which assesses biosimilarity on the basis of the totality of evidence.
Understand the similarities between biologic medicines and biosimilars in terms of structure, mode of action, efficacy and safety.
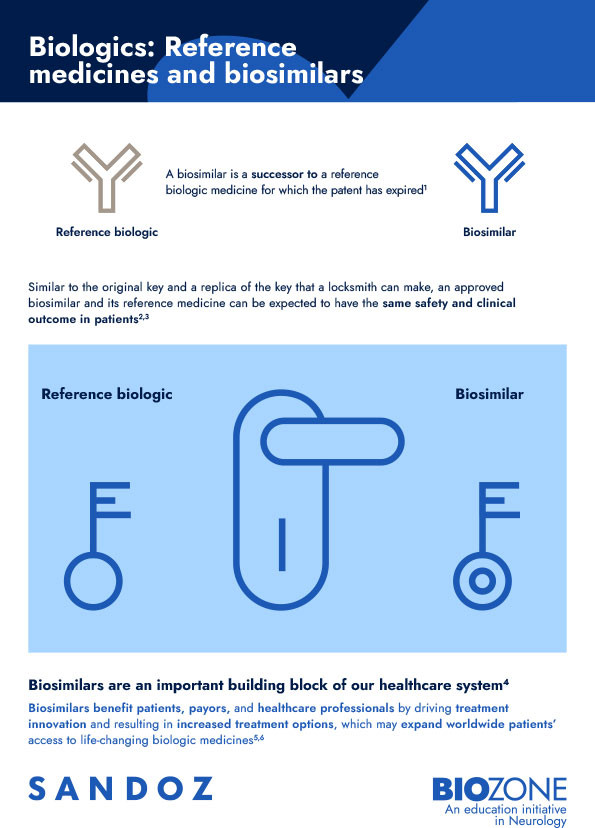
A biosimilar is a successor to a biologic medicine – also called the ‘reference medicine’ – whose patent has expired.1 Similar to the original key and a replica of the key that a locksmith can make, both the existing biologic medicine and its biosimilar produce the same therapeutic effect.2,3
A biosimilar and its existing biologic are both structurally complex, share a mechanism of action and demonstrate equivalent efficacy and comparable safety.3
References:
1. Skingle D. RMD Open 2015;1(1):e000141.
2. Webster CJ, Wong AC, Woollett GR. BioDrugs 2019;33:603–11.
3. EMA. Biosimilars Information Guide. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/leaflet/biosimilars-eu-information-guide-healthcare-professionals_en.pdf. [Last accessed April 2022];
These materials are intended for healthcare professionals only. This page is sponsored by Sandoz.
MLR: 215945
This infographic highlights the strictly regulated biosimilar approval process, which assesses biosimilarity on the basis of the totality of evidence.